What are the Joints?
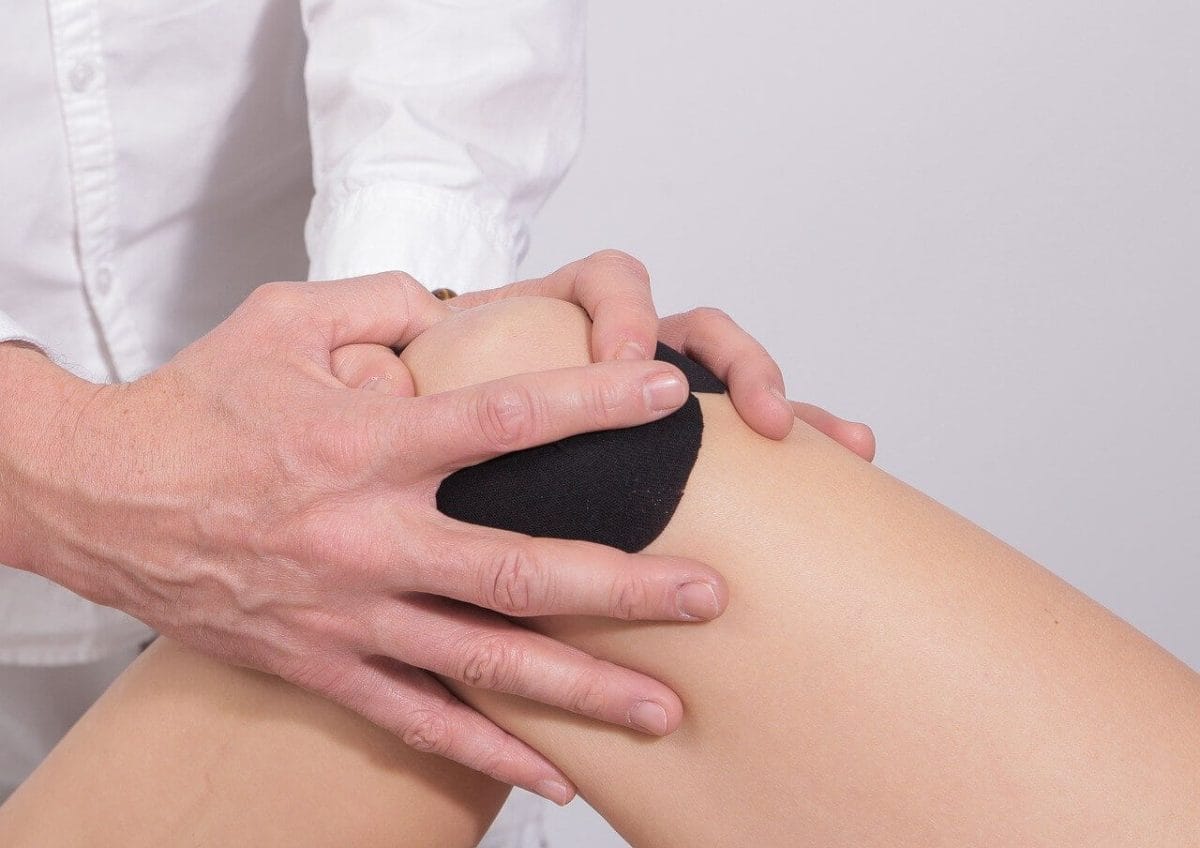
A joint or articulation is the connection made between bones in the body which link the skeletal system into a functional whole. They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements
The 10 Effects of Aging Changes
- People lose bone mass or density as they age, especially women after menopause. The bones lose calcium and other minerals.
- The spine is made up of bones called vertebrae. Between each bone is a gel-like cushion (called a disk). The middle of the body (trunk) becomes shorter as the disks gradually lose fluid and become thinner.
- Vertebrae also lose some of their mineral content, making each bone thinner. The spinal column becomes curved and compressed (packed together). Bone spurs caused by aging and overall use of the spine may also form on the vertebrae.
- The foot arches become less pronounced, contributing to a slight loss of height.
- The long bones of the arms and legs are more brittle because of mineral loss, but they do not change length. This makes the arms and legs look longer when compared with the shortened trunk.
- The joints become stiffer and less flexible. Fluid in the joints may decrease. The cartilage may begin to rub together and wear away. Minerals may deposit in and around some joints (calcification). This is common in the shoulder.
- Hip and knee joints may begin to lose cartilage (degenerative changes). The finger joints lose cartilage and the bones thicken slightly. Finger joint changes are more common in women. These changes may be inherited.
- Lean body mass decreases. This decrease is partly caused by a loss of muscle tissue (atrophy). The speed and amount of muscle changes seem to be caused by genes. Muscle changes often begin in the 20s in men and in the 40s in women.
- Lipofuscin (an age-related pigment) and fat are deposited in muscle tissue. The muscle fibers shrink. Muscle tissue is replaced more slowly. Lost muscle tissue may be replaced with tough fibrous tissue. This is most noticeable in the hands, which may look thin and bony.
- Muscles are less toned and less able to contract because of changes in the muscle tissue and normal aging changes in the nervous system. Muscles may become rigid with age and may lose tone, even with regular exercise.
Here are 5 tips to protect your joints
1. Stop smoking if you are a smoker!
Smoking and tobacco use are risk factors for everything from cardiovascular problems to cancer. Smoking can hamper your joints, too.
2. Replace energy drinks and soda with water
Water makes up about 80% of your body’s cartilage (the flexible, connective tissue that cushions your joints). If you don’t stay well-hydrated, your body will pull water from cartilage and other areas
3. Don’t let extra weights overtax your joints
Your joints are meant to sustain a certain amount of force. If you are overweight or underweight, you’re likely putting more stress on your joints. A hearty mix of fruits and vegetables, as well as whole grains and healthy fats, can help to reduce your inflammation and protect your heart.
4. Always warm-up and cool down
If you skip the warm-up and start your exercise will put your joints at greater risk of strain and overloading. For the best result, we recommend the warm-up and cool-down exercise should take at least five minutes. Work with the same muscles you will use during exercise, but at a slow pace. Warm-up exercise is most important as you age because older joints are often less resilient.
5. Taking joints supplement – Quan Wei Active Joint

Quan Wei Active Joint is made from a blend of minerals formula (Glucosamine Sulfate, Chondroitin, MSM) and herbs (Morinda, Epimedium, Sambucus, etc.). Glucosamine is commonly taken in combination with chondroitin to help patients suffering from joint problems, particularly those who suffer from osteoarthritis.
How will Quan Wei Active Joint benefit me?
- Regenerates and repair cartilage cells
- Recondition joint function
- Support articular cartilage
- Improve cartilage’s elasticity
- Control the balance of the synovial fluid secretion
- Enhances liver vitality
- Combats poor calcium absorption
How to use: Take twice daily, 2 capsules each time.
Packing size: 90+30 capsules.